Heterofuctionalisation of C=C and C-H bonds
Enantioselective aza-Michael reactions
Dicationic (BINAP)palladium(II) complex induced high enantioselectiviies in the addition of primary (and secondary) aromatic amines to N-alkenoyl oxazolidinones (up to 93% ee), imides (89% ee), and carbamates (>99 % ee).
The mechanism of these reactions was examined fusing a combination of techniques, including X-ray crystallography, mass spectrometry, NMR, UV/Vis spectroscopy, and kinetic studies. The study culminated in the design of a new reaction protocol, which was subsequently applied to the synthesis of torcetrapib, a drug being developed to treat hypercholesterolemia.

Enantioselective alpha-hydroxylation of 1,3-diketones
Concepts developed in the above were extended to the heterofunctionalisation of the acidic C-H present in 1,3-ketoesters. Using dicationic Pd(II) as a catalyst, very high ee's (up to 98%) can be achieve in the alpha-hydroxylation of 1,3-ketoesters. To this date, these records remained unsurpassed.
The stereoselectivity was rationalized by transition state modeling, which revealed a number of cooperative weak interactions between oxidant, ligand and counterion, together with C-H/pit interactions that cumulatively account for the unusual stereoselectivity.

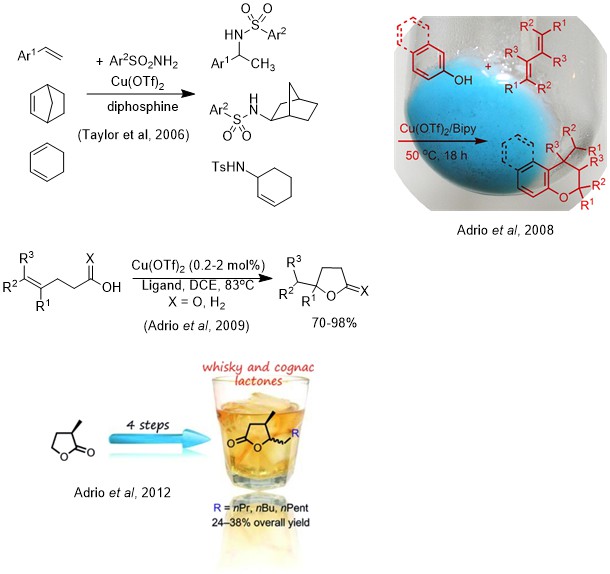
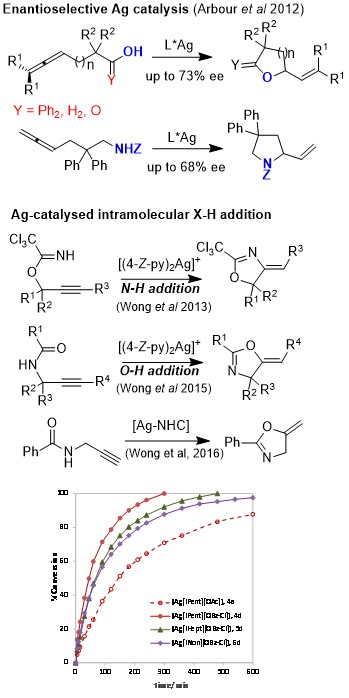
Copper Catalysis
The use of cheap Cu(II) catalysts for N-H and O-H addition to C=C bonds. We have developed a number of methodologies that can be used for the synthesis of biologically interesting heterocyclic molecules.